We do NOT recommend sharing administrator access to your website with anyone. If you are a managed hosting client, please check with our development team before delegating administrator access to avoid a security lockout on your website or server.
Do you want to better understand WordPress user roles and permissions?
WordPress comes with a user role management system that defines what a user can and can’t do on your website. Knowing these user roles and permissions are essential as your WordPress site grows.
In this guide, we’ll go in depth into WordPress user roles and permissions, so you can better manage your site.
What Are WordPress User Roles and Permissions?
Using WordPress user roles and permissions the right way gives you complete control over your WordPress website and can help improve your website security.
Users are people who have already registered on your site, and every user is assigned a specific role when their account is created.
A user role is made up of certain capabilities, or permissions, that spell out the actions they can take on your website.
Out of the box after you install WordPress, there are five default user roles available:
- Administrator
- Editor
- Author
- Contributor
- Subscriber
You can see a full visual comparison between each user role by viewing this downloadable infographic.
Alternatively, you can read the summary of each user role and their capabilities and permissions below.
1. Administrator Role
On a regular WordPress website, the administrator role is the most powerful user role. Users with the administrator role can add new posts, edit posts by any users, and delete those posts.
Plus, they can install, edit, and delete plugins and themes.
Most importantly, admin users can add and delete users, and change information about existing users, including their passwords.
This role is basically reserved for site owners and gives you the full control of your WordPress blog. If you are running a multi-user WordPress site, then you need to be very careful who you assign an administrator user role.
2. Editor Role
Users with the editor role in WordPress have full control on the content sections your website.
They can add, edit, publish, and delete any posts on the site, including the ones written by others. An editor can moderate, edit, and delete comments as well.
Editors do not have access to change your site settings, install plugins and themes, or add new users.
3. Author Role
Users with the author role can write, edit, and publish their own posts. They can also delete their own posts, even if they are already published.
When writing posts, authors cannot create new categories, but they can choose from existing ones. They can also add tags to their posts.
Authors can view comments even those that are pending review, but they cannot moderate, approve, or delete any comments.
They do not have access to site settings, plugins, or themes, so it is a fairly low-risk user role. The only exception is the ability to delete their own published posts.
4. Contributor Role
Users with the contributor role can add new posts and edit their own posts, but they cannot publish any posts.
When writing posts they can choose from existing categories and create their own tags.
The biggest disadvantage of the contributor role is they cannot upload files, so they can’t add images to their posts.
Contributors can also view all website comments, but they cannot approve or delete comments.
Finally, they don’t have access to website settings, plugins, or themes, so they cannot change any settings on your site.
5. Subscriber Role
Users with the subscriber role can login to your WordPress site, update their user profiles, and change their passwords.
They can’t write posts, view comments, or do anything else inside your WordPress admin area.
This user role is particularly useful if you have a membership sites, online store, or another site where users can register and log in.
If you want to create a custom login experience for your visitors, then see our guide on how to add a front-end login page and widgets in WordPress.
Bonus: Super Admin Role
This user role is only available on a WordPress multisite network.
Users with the super admin user role can add and delete sites on a multisite network. They can also install plugins and themes, add users, and perform network wide actions on a WordPress multi-site setup.
Think of it like having admin access to every single site in the network.
How to Customize Existing User Roles and Permissions in WordPress
The default WordPress user roles have capabilities that will work for most WordPress websites and blogs.
For example, if you run a magazine website, then the ‘Editor’ role can be assigned to senior staff, the ‘Author’ user role can be for junior staff, and the ‘Contributor’ role can be for guest writers.
But sometimes you might want to customize the permissions and capabilities assigned to the role for the specific needs of your website.
Like the default author role that lets users publish their own posts and also gives them the ability to delete their published posts. In this case, you may want to remove the capability that lets authors delete their posts.
There are some plugins that add specific roles to your website, such as a comment moderator user role plugin.
But if you want to customize your WordPress user roles, the easiest way is by using the Members plugin. It lets you simply create, manage, and change user roles across your website.
First thing you need to do is activate and install the plugin. For more details, see our step by step guide on how to install a WordPress plugin.
Upon activation, you’ll have a new menu item called ‘Members’ in your WordPress admin panel.
You need to go to Members » Roles and then click on the user role you want to edit.
In this example, we will be editing the ‘Author’ role, but you can choose the best role for your needs.
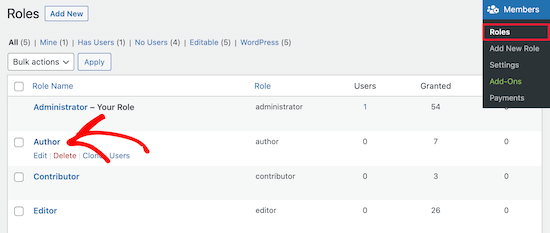
This brings you to a screen where you can fully customize the capabilities for that role.
To remove a capability for the role, simply check the ‘Deny’ box. If you want to add a new capability, then check the ‘Grant’ box.
Here, we will check the ‘Deny’ box for the Delete Posts user capability.
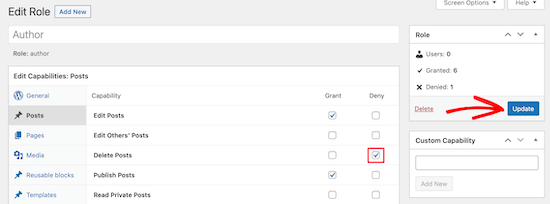
If you don’t check a box for an available role, then that user won’t have that capability.
Once you’re finished customizing your role, make sure to click the ‘Update’ button.
The changes you make will automatically apply to all existing users who have that role and all new users the role is assigned to.
How to Create Custom User Roles in WordPress
Another thing you can do is create completely custom user roles in WordPress with unique sets of capabilities.
To do this, we will be using the same plugin as above.
Simply navigate to Members » Add New Role and then give your new role a name.
In this case, we’ll create a developer role that we can give to a WordPress developer with certain permissions granted.
The left-hand column has different sections that have lists of available capabilities. We’ll select the ‘Appearance’ tab and then add capabilities to edit, install, and update themes.
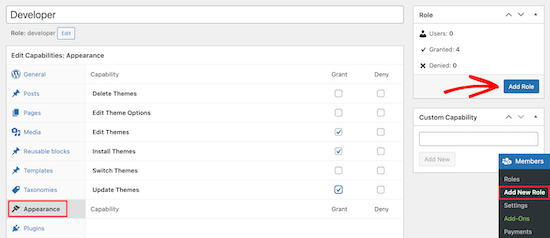
After that, make sure to click the ‘Add Role’ button to save the user role.
Next, you can create a new user and assign that user the new role.
To do this go to Users » Add New and then fill in your new user information.
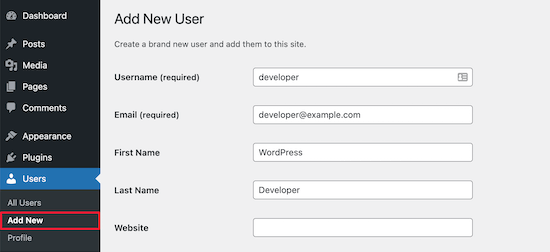
At the bottom of the screen, you’ll see a ‘User Roles’ section.
Simply check the boxes for the user roles you want to assign to the new user and then click the ‘Add New User’ button.
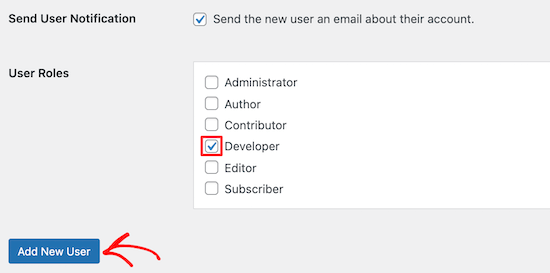
Now, you’ve created a new custom WordPress user role and assigned it to a new user.
For more details, see our guide on how to add new users and authors to WordPress.
If you want to create a WordPress user role that’s only for moderating comments, then see our guide
We hope this article helped you understand user roles and permissions associated with each type. If you have questions about adding someone to your website to collaborate, reach out to our support team.
Was this article helpful?
That’s Great!
Thank you for your feedback
Sorry! We couldn't be helpful
Thank you for your feedback
Feedback sent
We appreciate your effort and will try to fix the article